MIT 18.06(Linear Algebra) L1 Note
Lecture 1: The geometry of linear equations
1. Mind Map

2. Reading Notes (1.1-2.1)
Chapter 1 Introduction to Vectors
$$ \text{Linear combination} \quad c\vec{v}+ d\vec{w}= c \begin{bmatrix} 1\cr 1\end{bmatrix} +d \begin{bmatrix}2\cr 3\end{bmatrix} =\begin{bmatrix}c+2d\cr c+3d\end{bmatrix} $$
- 1.1 Vector addition $v+w$ and linear combinations $cv+dw$.
- 1.2 The dot product $v · w$ of two vectors and the length $\lVert v \rVert = \sqrt{v \cdot v}$
- 1.3 Matrices A, linear equations $Ax=b$, solutions $x = A^{-1} b.$
1.1 Vectors and Linear Combinations
- Vector Addition
- Scalar Multiplication
1.2 Lengths and Dot Products
- Dot product / Inner Product is the number of $\vec{v}\cdot \vec{w}$
- $\vec{v}= (v_1,v_2), \vec{w}= (w_1,w_2)$
- $\vec{v}\cdot \vec{w} = v_1w_1 +v_2w_2$
- Dot product = 0 → Perpendicular vectors
- Order makes no difference.
- Lengths and Unit Vectors
- length = $\lVert v \rVert = \sqrt{v \cdot v} = (v_1^2 + v_2^2 \cdots +v_n^2)^{1/2}$
- unit vector u is a vector whose length equals one
- Unit vector $u = v / \lVert v\rVert$
- Cosine Formula: If v and w are nonzero vectors then $\frac{v \cdot w}{\lVert v\rVert\lVert w\rVert} = cos\theta$
- Schwarz Inequality $|v \cdot w| \leq \lVert v\rVert\lVert w\rVert$
- Triangle Inequality $\lVert v+w\rVert \leq \lVert v\rVert + \lVert w\rVert$
- Geometric mean $\leq$ Arithmetic mean : $\sqrt{xy} \leq \frac{x+y}{2}$
- *Cosine Formula: $cosine = v\prime * w / (norm(v)norm(w))$
- The arc cosine: angle = acos(cosine)
1.3 Matrices
-
Matrix times vector: Combination b of columns of A
(matrix A acts on the vector x)
$$ Ax = \begin{bmatrix}1&0&0 \cr -1&1&0\cr 0&-1&1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix}x_1 \cr x_2\cr x_3 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}x_1 \cr x_2-x_1 \cr x_3-x_2 \end{bmatrix} $$
-
Ax is also dot products with rows
$$ Ax = \begin{bmatrix}1&0&0 \cr -1&1&0\cr 0&-1&1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix}x_1 \cr x_2\cr x_3 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}x_1 \cr x_2-x_1 \cr x_3-x_2 \end{bmatrix}= \begin{bmatrix}(1,0,0)\cdot(x_1,x_2,x_3) \cr (-1,1,0)\cdot(x_1,x_2,x_3) \cr (0,-1,1)\cdot(x_1,x_2,x_3) \end{bmatrix} $$
-
Linear Equations
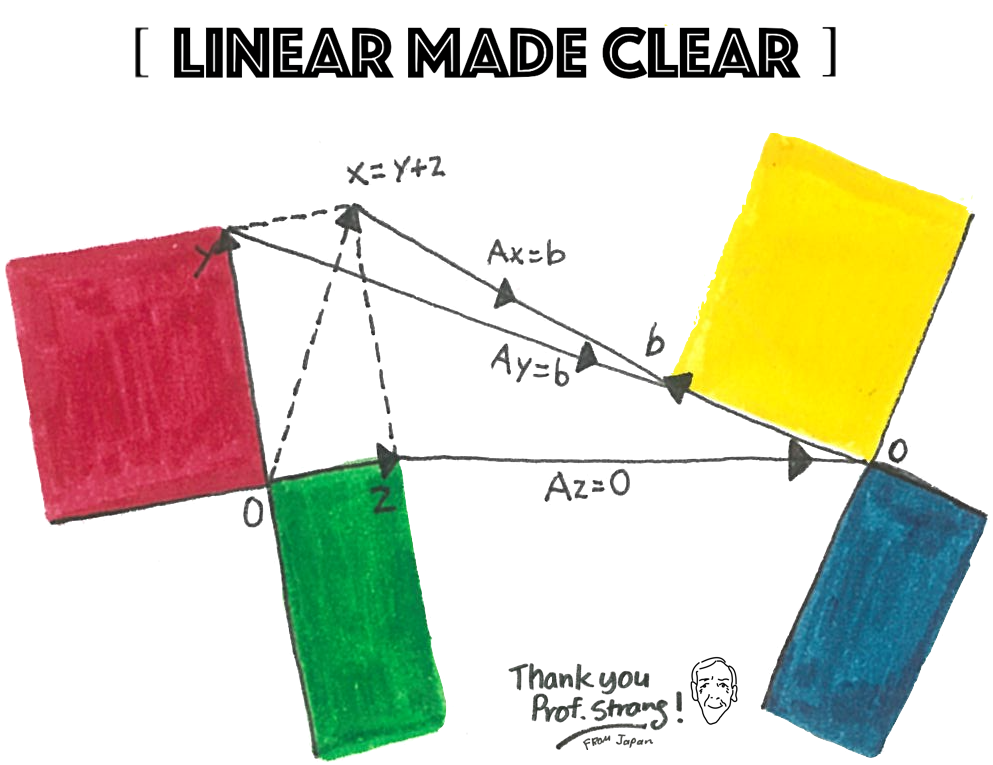
- new viewpoint: Q: Which combination of u, v, w produces a particular vector b?
- Inverse problem: how to find the input x that gives the desired output b = Ax
- $\text{Equations: }Ax=b\quad \text{Solution: }x=A^{-1}b$
- matrix A is “invertible”
- Independence and Dependence
- Independent columns: Ax=0 has one solution. A is an invertible matrix.
- Dependent columns: Cx = 0 has many solutions. C is a singular matrix.
Chapter 2 Solving Linear Equations
2.1 Vectors and Linear Equations
-
Two equations, two unknowns
- Row Picture
- Column Picture
- Coefficient matrix
-
The Matrix Form of the Equations
- Multiplication by rows. (dot products)
- $Ax = \begin{bmatrix}(row1)\cdot x \cr (row2)\cdot x \cr (row3)\cdot x \end{bmatrix}$
- Multiplication by columns (combination of columns)
- $Ax = x(column1) +y(column2) +z(column3)$